Data Centre Management
A datacentre operator can plug CACTOS to enact performance optimisations in his datacentre. It is as easy as plug a new device to the power. In CACTOS we have developed a toolkit that was developed mainly upon OpenStack. But, also can be enacted using other cloud middleware tools.
Moving to the architecture, the OpenStack VMI and OpenStack VMI Controller enable CACTOS functionality for OpenStack-based Cloud Installations (cf. Figure 1). VMI enhances the default OpenStack REST interface to users so that they can also trigger application deployment. In addition, it intercepts calls to the standard OpenStack interface dealing with spawning and terminating virtual machines. The VMI Controller in turn executes tasks defined by CACTOS (mainly CactoOpt) on the data centre to enact optimisation decisions. The main component, which handles flows between CACTOS and an OpenStack Cloud Platform, is the Runtime Management.
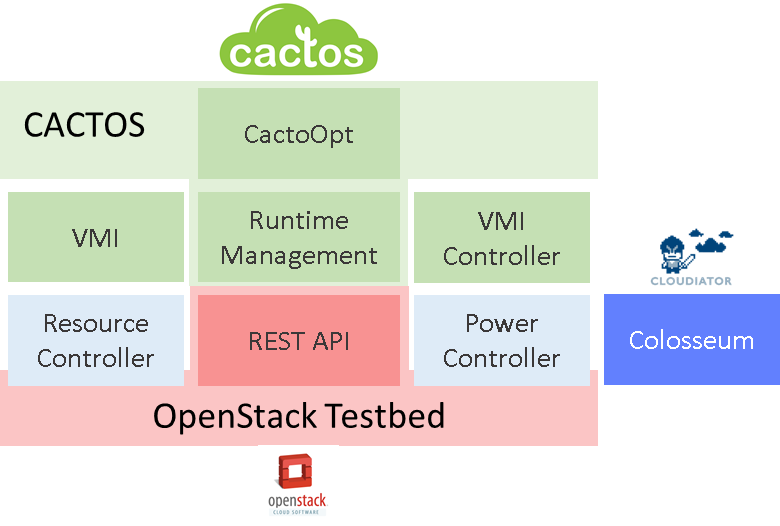
Figure 1: CACTOS Architecture on an OpenStack-based datacentre
In detail, incoming REST requests to VMI are translated from OpenStack format to a generic CACTOS format and then passed to the Runtime Management. CactoOpt as well as the Runtime Management component use the VMI Controller to execute CACTOS generic tasks in an OpenStack specific way. The VMI controller may issue requests to the OpenStack REST API, or to one of the two proxy services for controlling physical resources and power state of compute nodes in the OpenStack data centre. For application instance deployment, CACTOS uses Cloudiator, a multi-cloud application orchestration software. The VMI and the VMI Controller communicate with Cloudiator’s Colosseum service to handle actions on application level.